Tulips are one of the most beautiful flowers decorating spring gardens and summer cottages. Their variety is very large, and one of the most decorative is the Foxy Foxtrot variety. The plant is often used in landscape design, since, in addition to aesthetic appeal, it is characterized by low environmental requirements. Nevertheless, a gardener who has decided to plant this variety on the site needs to know about some of the features of cultivation.
Grade description
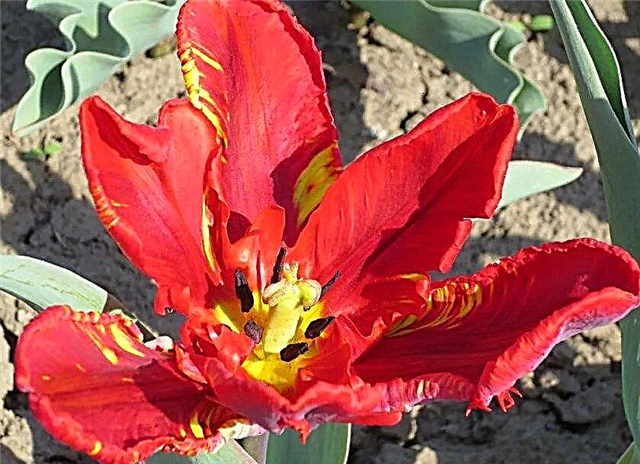
It is impossible not to miss the Foxy Foxtrot tulip in the garden, an adult flower is able to reach a half-meter height and, thanks to a strong peduncle, proudly hold the posture throughout the flowering period. Goblet-shaped buds deserve special attention. They are quite large - in the open state, the flower has a diameter of up to 10 cm. The color of the petals is very delicate, creamy pink, the inflorescence is yellow with a slight pinkish coating. A characteristic feature of this variety is a slight terry buds.
Variety Foxy Foxtrot belongs to the early. Tulips bloom already in mid-April (with a very warm spring, flowering can begin at the beginning of the month), and the flowering period lasts about 2-3 weeks, after which trihedral boxes with seeds ripen inside the buds. The root system of the plant consists of subordinate roots produced by the bulb. At the end of the season, they die off, but at the same time young bulbs are formed, which, after the flowers wither, are separated and transplanted.
Did you know? Tulip buds also sleep in the dark. In the evening, they close and open only at sunrise.
Growing Features
Tulips are easy to propagate at home. To do this, after flowering, plants are dug up and daughter plants are separated and separated from the main bulb, which are then planted as an independent planting material. However, when planting, many nuances should be taken into account so that the culture takes root safely.
Landing rules
For planting the Foxy Foxtrot variety, you should choose a well-lit area, protected from strong gusts of wind. Try to find a place with a low occurrence of groundwater or arrange a drainage pillow at the landing site so that the water does not stagnate. It is better to plant bulbs in the cool period when the temperature of the soil layer drops to + 5 ... + 7 ° С.

The optimal time is the end of September. If you plant in warm soil, the bulbs will take root much more slowly. Tulips prefer fertile soils, loams or sandstones with low acidity. First you need to dig the area to a depth of 30 cm, remove all weeds along with the roots. Then the soil is fertilized: for each square meter, 2 buckets of compost or humus, 1 glass of wood ash and 60 g of phosphorus-potassium fertilizing. All these procedures are preferably carried out at least 1 month before planting.
Important! You can not organize a flower bed with tulips in the area where other bulbous plants that have common diseases and pests with the culture have been grown for the last 5 years.
Tulips are planted in rows, observing a distance between them of at least 20 cm. The interval between the bulbs in the row should be 10–15 cm. It is advisable to add complex mineral fertilizers (100 g per 1 m²) and a 5-centimeter layer of river sand to the dug planting grooves with a depth of about 20 cm, which will protect the bottom of the bulb from infections and decay.

Inspect the material well before planting. If you notice signs of rotting or infection, discard such bulbs, and process suitable ones for 1 hour in a 0.5% solution of potassium permanganate and dry. Prepared bulbs are planted in furrows, covered with soil (do not tamp!) And watered abundantly. Closer to winter, the planting is mulched with peat or sawdust. In the spring, the shelter is removed, the site is carefully weeded and waiting for the first shoots.

The subtleties of care
Tulips of the Foxy Foxtrot variety are unpretentious, so they can be found not only in private farms, but also in city parks and squares. However, if you want to see your plants healthy and luxuriantly flowering, it is recommended that you still provide them with some care.
In particular, this applies to procedures such as:
- Watering. Tulips love moisture, but do not withstand waterlogging of the soil, leading to rotting of the bulb. The best way is to dig out the grooves in the row-spacings, water them abundantly and bury them in order to retain moisture. Watering is carried out as necessary. In rainy periods they are not needed at all, and in dry periods it should be ensured that the soil does not dry out.
- Weeding and digging. Immediately after planting the bulbs, it is important to ensure that the beds are not populated by weeds. It’s better to remove annoying “guests” manually, as glanders can damage the bulbs. Weeding should be carried out and the entire subsequent period of growth and vegetation. Also, the earth is periodically loosened and dug up so that moisture penetrates better into it, and also to avoid thickening, which often leads to the development of diseases.
- Top dressing. When choosing a fertilizer for tulips, keep in mind that they have very thin roots. You can not introduce aggressive top dressing into the soil, such as chlorine-containing compounds or unripe manure that can burn them. Soluble fertilizers are mainly used and applied along with irrigation. The first feeding is carried out when the leaves unfold. During this period, plants need complex mineral compositions with a high content of potassium and phosphorus, as well as the presence of a small amount of nitrogen in the composition. In the future, top dressing can be repeated during periods of budding and flowering. It is recommended to add superphosphate and potassium nitrate as top dressing.
- Pruning. In this case, we are talking about removing the petals when they begin to fade. This should be done carefully, manually, so as not to touch the stem and not damage it. If you do not carry out this procedure, it is likely that the underground bulb will weaken and not stockpile the necessary nutritional compounds. If you cut flowers for a bouquet, try to leave as many leaves on the stem as possible - so the root bulb will be much larger.
- Preparing for the winter. Tulip bulbs can be dug up annually, stored in the refrigerator all winter, and transplanted to a new place in the spring - so the plants will develop and bloom better. However, not all gardeners are inclined to such a painstaking process and are engaged in transplanting tulips every 3-4 years. So that tulips can be wintered safely, in moderate latitudes, planting is covered with a layer of mulch up to 7 cm from sawdust or peat. In the northern regions, it is recommended, in addition to mulch, to use any non-woven material (burlap, spanbond, etc.) for shelter.
 During watering, water droplets should not be allowed to fall on leaves and buds, otherwise spots may appear and flowers will fade without opening.
During watering, water droplets should not be allowed to fall on leaves and buds, otherwise spots may appear and flowers will fade without opening.
Pests and diseases
A sad fact for tulip lovers is a large number of diseases that can harm the plant. In science, there are about 30 and almost all infectious ones.
Most often, tulips suffer from such ailments as:
- gray rot - Diseases are caused by fungi, which can lead to damage only to aboveground stems, or damage the bulb. The disease can be recognized by small brown and yellow spots on the foliage, which grow and merge over time, and then a white coating appears. Rot most often progresses in wet weather, and is carried by air;

- typhulosis - A disease in which the bulbs and roots of tulips rot. The causative agent is the fungus Typhula borealis. With damage, the shoots of the plant stop in development and become very small. The main carriers of infection are cereals and legumes;

- fusarium - A disease in which an infection attacks tulips through the soil. First, the bulb is damaged, as a result of which the culture begins to lag behind in growth. Often, bulbs rot, soften and die in the ground;
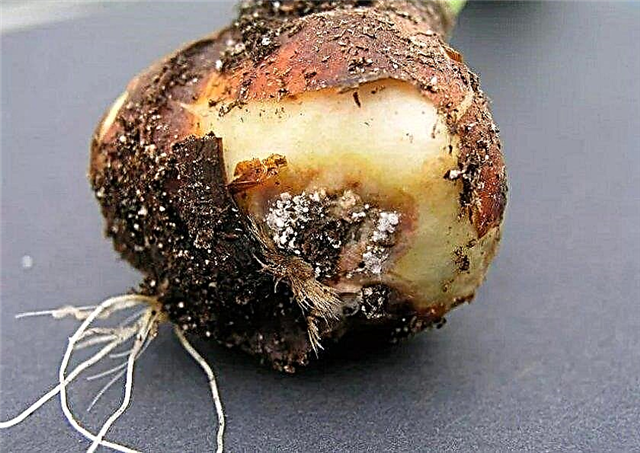

- variegation - is determined by the appearance on the leaves of small lime or silver touches. This viral disease is very slow and can weaken the plant from year to year. If measures are not taken in time, the tulip bulbs will fade and degenerate. The carriers of infection are harmful insects.

To minimize the risk of plant damage, you must follow the rules of agricultural technology: periodically dig and fertilize the soil, ensure the discharge of groundwater in wetlands. If you notice the signs of an ailment, first get rid of the affected specimens - remove them from the soil along with the rhizome and burn, and cover the holes with wood ash. Further, the soil is recommended to be disinfected with a 1.5% formalin solution.
In addition to diseases, tulips can attack harmful insects. One of the most dangerous pests is the onion tick. Already from the name it is clear that this small insect (less than 1 mm) affects the tulip bulb. The tick makes its way between the onion flakes and literally gnaws off the tissue, which leads to rapid decay. It is possible to determine the appearance of an insect by premature fall of foliage, deterioration in the quality of flowers.
Did you know? Calendula and Nasturtium secrete volatile — substances that kill pathogenic bacteria. Neighborhood with these plants will protect tulips from ailments.
Affected plants should be removed from the beds, and the rest of the flowerbed should be thoroughly sprayed with a 0.2% solution of Celtan. Another dangerous pest is the aphid, which infects leaves, stems and peduncles, feeding on the sap of the plant. In addition, it is a carrier of viral diseases, so you need to eliminate it from the garden immediately. In this case, treatment with Confidor, Aktara according to the instructions will help.
Tulip in landscaping
High decorative culture often makes it the main participant in the landscape composition. It is very beneficial to plant early tulips in the company of perennials. The advantage of this planting is the flowering sequence. First, you will admire the variegation of tulip buds, and then, when they begin to fade, the lush green perennials will hide the yellowing leaves and eventually begin to show their beauty of flowering.
Thus, from early spring to late autumn, your flowerbed will demonstrate all its splendor. Excellent neighbors of tulips Foxy Foxtrot will be crocuses, hyacinths, primrose, pansies, daisies. Mixborders from such a “company” are planted in recreation areas, at gazebos and benches. Do not forget about the coniferous representatives who successfully emphasize the spring mood.
 Often flowers are planted as a beautiful fence of paths on the site.
Often flowers are planted as a beautiful fence of paths on the site.
Given that tulips can be grown in separate containers, containers can be installed on the loggia, porch, turning the site into a chic flower garden. On a spring morning, they joyfully greet their hosts with warm tones of buds. By the way, landscape compositions are now very popular when in the middle of a green lawn some old object is installed (a wooden wheelbarrow or trolley, a barrel, a trough, etc.), in the cavity of which a flowerbed of fresh flowers is formed.
Tall tulips such as Foxy Foxtrot are perfect for this. Tulips are an ideal decoration for rocky gardens and rock gardens, giving picturesqueness to specific reliefs. Here they are successfully combined with ground cover plants, as well as coniferous trees and shrubs, such as yew, juniper, thuja, etc.
The purchase of early Foxy Foxtrot tulips is an excellent solution for a summer cottage. The culture is hardy and able to quickly adapt to climatic conditions, requiring only minimal care. And flowering, although it does not differ in duration, but leaves behind itself the most pleasant emotions.