Typically, seed potatoes harvested in the fall are used to plant potatoes on the site. But to update the varietal characteristics of this culture, it is recommended to grow it from seeds every 5-6 years. This article lists the best varieties of tubers for seed propagation, describes the methods of production and the rules for collecting potato planting material, as well as recommendations for its storage and preliminary preparation.
Methods for producing potato seeds at home
Potatoes grown from seeds have several advantages compared to vegetables obtained as a result of the standard planting of seed tubers in the soil. It is characterized by a more stable immunity to diseases and pests, and in the second year of cultivation it gives a generous harvest of tubers of the highest quality.
Did you know? In 1596, the Swiss botanist Caspar Baugin gave the potato its scientific name, Solanum tuberosum, which is still in use today.
You can get the seeds of this culture in two main ways:
Varieties of potatoes for seed propagation
Berries with seeds are formed on all potato bushes, but there are varieties that are best suited for seed propagation. They form the maximum number of fruits with high-quality planting material, characterized by high germination.
The best varieties of potatoes suitable for propagation by seeds include the following varieties:
- Assol. The first tubers can be dug up in mid-July, and the final harvest is carried out in August. Potatoes have an oval shape, with smooth skin of light tone. The internal structure of the vegetable is dense, pale yellow. It is resistant to diseases, resistant to sharp climatic changes. The yield is up to 3.5 kg per plant, the mass of tubers is from 100 g and above.

- Farmer. It takes no more than 65 days to ripen the crop, and from one bush you can collect about 10-15 potatoes covered with a thin light yellow skin. The mass of one tuber is up to 100 g, and the yield is up to 1 kg from each plant. The pulp of the vegetable does not break down during the cooking process, and the plants are resistant to viral diseases and compactly look on the beds.

- Triumph. The variety is characterized by early ripening and high productivity. The tubers are oval and medium in size, covered with pale yellow peel from the outside. From 1 ha of plantings, you can get up to 500 kg of potatoes, and on each bush up to 30 tubers are formed. The flesh of the vegetable is cream colored and is ideal for baking and making soups. The variety has good immunity to fungal and viral infections.

- Empress. Bushes of this species take up a little space on the bed, but give large tubers of an elongated shape with a flat surface. Their flesh is yellowish and tastes good. The crop yield is 3.2 kg from one bush, and the weight of one vegetable is 60–150 g. The first tubers can be dug up in July, and the final harvest is carried out in early autumn. The variety is resistant to fungal diseases and is rarely affected by a nematode.
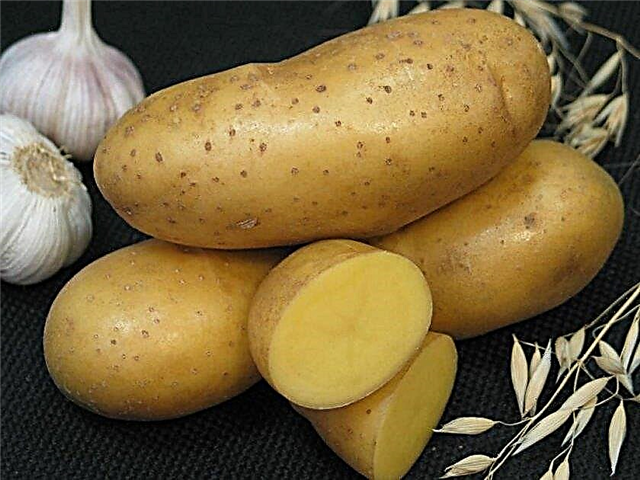

- Velina. Shrubs of this variety are characterized by a high growth rate and dense foliage. Harvest can be harvested in August. The tubers are oval and medium in size, and their peel and flesh are light yellow. The taste is high, vegetables can be used to prepare a variety of dishes. The variety is resistant to fungal and viral infections.
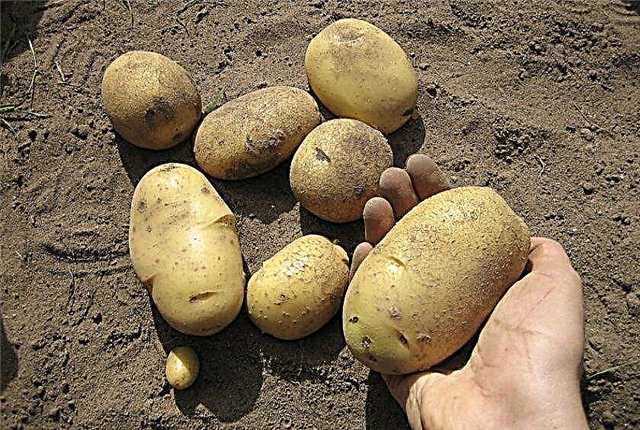

- Ilona. This variety fully ripens in August, but you can dig up young tubers from mid-July. Vegetables are elongated and large in size, and their skin is painted in beige. The white pulp is very tasty, during the cooking process it becomes friable. Potato has good immunity to common diseases and pests, it adapts well in different climates.
- Revenge. Plants of this variety have a powerful stem and give a high yield of large fruits, so they are often grown on an industrial scale. The tubers are round-oval in shape and large in size, each weighing about 120 g. The smooth peel is light yellow in color and the creamy flesh has an excellent taste and does not darken during the heat treatment. The variety has a good immunity to diseases and is rarely affected by pests.

- Beauty. The variety belongs to mid-season and has a high yield - up to 450 c / ha. Bushes are tall and erect, covered with dense foliage. The tubers are large in size and their peel is colored red. The mass of one vegetable is 250-300 g. The pulp has a light yellow color and excellent taste, perfectly retains shape when frying and baking. Potato is resistant to fungal diseases and adapts well to adverse weather conditions.
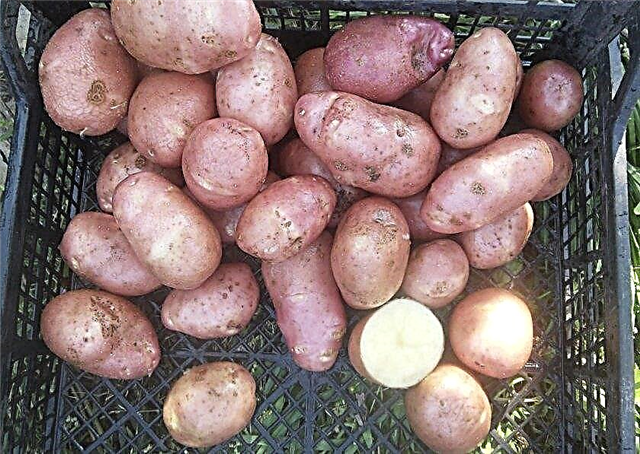

- Lada. Plants are compact in size, and in August they give a good harvest of round fruits, which are perfectly stored in winter. The smooth peel of the tubers is painted in a pale yellow or reddish color, and the flesh contains a lot of starch and has a white-yellow color. The yield of the variety is up to 400 kg / ha, and the weight of one tuber is up to 150 g. Potatoes of this species have a strong immunity to common infections and can be used to make chips.

- Virgo. Plants are small in size and average in leaves. The tubers are covered with a pale red smooth peel, and their flesh is yellow and boils well. Vegetables are large and elongated, each weighing 100–150 g. The variety is resistant to various infections and pests.

When to collect potato seeds
After flowering is complete, small round berries - bulbs appear on the potato bushes. They are small in size and initially painted light green in color, and become dark brown as they mature.
To successfully collect seeds, it is recommended that potato bulbs be picked from the bush slightly immature. It is best to carry out this procedure in the first half of July, when the surface of the berries still has a light green color.
Did you know? One of the most interesting types of potatoes is the Linzer Blaue variety - its fruits have a blue peel and flesh.
How to collect potato seeds from bulbs
In general, the process of self-harvesting potato seeds is very similar to the collection of tomato seed material. The number of berries on one bush depends on the variety and can reach several tens. Each bulb contains up to 200 small seeds.

Step-by-step instructions for self-collecting potato seeds are presented below:
- Tear off the round berries from the plant, and then spread them out in a thin layer or hang them in a gauze bag in a warm and well-lit room. For complete ripening and final softening of the fruit, several weeks are needed.
- Grind soft bulbs to a mushy state, and then add a little water to the mass. Put the mixture in a warm place for 2-3 days, for fermentation.
Important! In the process of fermentation, the dense shell of potato seeds is destroyed, which contains inhibitors - special substances that prevent the rapid germination of planting material.
- The main signs of the successful completion of fermentation are a specific pungent odor and the appearance of small air bubbles on the surface of the mixture.
- Fill fermented mass with water. High-quality planting material, in this case, will sink to the bottom of the tank, and defective seeds will float to the surface of the liquid.
- Strain the resulting liquid mass through a fine sieve or gauze, folded in several layers to separate the potato seeds from the water.
Video: How to Collect and Harvest Potato Seeds
Dates of harvesting and harvesting potato seeds
The exact timing of picking berries with potato seeds depends on the particular variety of the crop. Early ripe varieties ripen earlier, therefore, the fruits on them can form as early as June, and on plants with a late ripening period, berries appear closer to mid-July.
The general rule is that berries from potatoes need to be picked immediately after the bush begins to turn yellow and dry. After the seeds are separated from the pulp of the berries, they are prepared for storage.
Important! Properly harvested potato seeds can be stored for up to 6–10 years, but the highest germination rate is typical for planting material, whose age does not exceed 2 years.
To do this, perform the following actions:
- the seed material is washed under a stream of clean water to remove residual fruit pulp;
- moist planting material is laid out in a thin layer on thick paper and placed in a warm room for drying;
- dried seeds are packaged in paper envelopes, indicating the name of the variety and the date of harvesting on the packaging.
Storage and preparation for boarding
Harvested and packaged potato seeds should be stored at an air temperature of +12 ... + 16 ° C, protecting them from moisture. Packages with planting material should be protected from rodents and insects, which can damage them and make seeds unsuitable for sowing.

Potatoes can be grown from seeds in seedlings and seedlings. In the first case, sowing is carried out in individual containers for growing seedlings, and in the second case, planting material is embedded directly in open ground.
To accelerate the emergence of seedlings, it is recommended to prepare potato seeds before planting using the following actions:
- warm the seeds in a humid chamber at a temperature of +40 ° C for 15-20 minutes - this procedure will awaken the seeds;
- instead of preheating, you can soak the potato seeds in warm water for 48 hours;
- dry planting material in a warm room to a state of flowability;
- wrap potato seeds in a damp cloth for germination - they are kept at room temperature during the day, and cleaned on the bottom shelf of the refrigerator at night. The process of germination takes 10-14 days, and the tissue, at the same time, is periodically moistened so that it does not dry out;
- with the appearance of small sprouts on the seeds, they must be immediately embedded in the soil.
Growing potatoes from seeds requires additional efforts from the gardener, but it allows to increase the crop yield and makes it more resistant to various diseases. Using the recommendations listed in this article, you can choose the best potato variety for seed propagation, independently collect and prepare planting material, as well as properly prepare it for subsequent planting.