Larch is a tree from the Pine family that dumps needles for the winter. Before this, the needle-shaped leaves change the green color to yellow. The plant has a wide variety of beautiful decorative forms, so they like to grow them in gardens and parks. For planting, it can be propagated at home in several ways.
Methods of reproduction of larch at home
Deciduous coniferous tree can reproduce in two ways: vegetative and generative. Moreover, it is impractical to cut the plant. The stem, both in the wild and during home breeding, rarely forms roots, or does not form a root system at all. Shoots also take root slowly. Seed propagation is the most productive and fastest.
Did you know? When the larch wood dries, its density increases so much that it is impossible to hammer nails into a log. If the fastening reinforcement was driven into old larch boards, it is impossible to get it, because metal connection breaks.
Cuttings
Cuttings are practically not used, since the method rarely gives a positive result. Cuttings reluctantly take root.
However, for those who wish to apply this method, it is necessary:
- Choose one healthy branch.
- In the middle of the handle, make an incision in the bark and sprinkle with a growth stimulator. You can use "Kornevin."
- Next, the branch bends to the ground and sprinkles with a substrate.
- A plant fragment can “jump out” out under the pressure of a branch, therefore it is pressed with something.
- The incision is covered with sphagnum with moist moss and wrapped over the film.
- The moisture of the moss must be controlled throughout the summer so that the sprouted roots do not dry out and die. Roots are not separated from the parent plant until the next spring season.
- Cuttings with the root of the second year are cut from a branch and planted in a permanent place.

The method does not always give a positive result, since larch is difficult to cut. Getting a viable seedling is great luck.
Important! It is necessary to remove weeds around the larch shoot in a timely manner, since most ordinary grass can interfere with tree growth.
Propagation by layering
This method of reproduction is well suited for dwarf, creeping and low varieties. Sections of future seedlings are obtained by rooting branches that touch the ground and are partially dusted with moist soil.
Rooting shoots is quite simple, but for this you need:
- Choose a twig that grows below everyone to the ground.
- Bend it to the substrate.
- Fasten.
- Sprinkle with moistened soil.

The future seedling sprouts in 3-4 months (as the roots form). It is impossible to separate and transplant layering from the mother plant in the first year. Another season they should overwinter with the parent plant so that the root system can fully develop. Only next year, young larch can be separated and placed in a permanent place. A successful landing period is the end of summer or early spring.
Did you know? A fresh log house of a larch tree is drowning in water, therefore it can only be transported by land.
Seed propagation
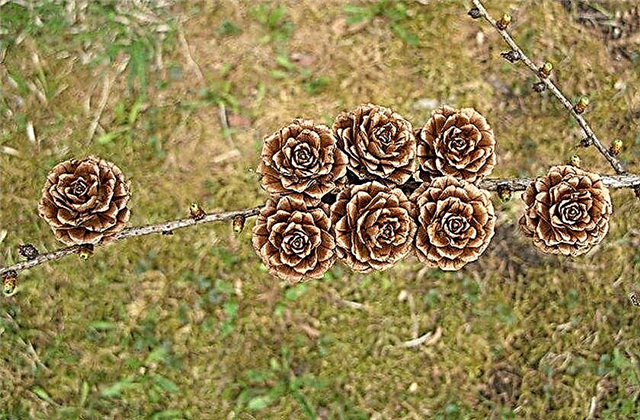
Seeds are in cones that open in spring or autumn. For home cultivation of both decorative forms of larch and wild varieties, cones can be collected in a park, square or forest. In some species of larch, cones do not come off completely, so you have to get the seed from it yourself and very carefully so as not to damage it.
Seed propagation is the most rational and fast method, which takes place in several stages:
- Seeding. Autumn seeds guarantee a greater percentage of germination than the spring crop. For the selection of seed, cones with tightly pressed scales of a lighter shade are chosen before the seeds begin to spill out.

- Preparing for the landing. Seeds are placed in a container with cold water for 1-2 days to sort empty grains (they float to the surface). “Full” seeds sink to the bottom. Then for 2 hours the seed is placed in a solution of potassium permanganate, fungicides or hydrogen peroxide for processing, and then washed with clean water.

- Stratification. The procedure is performed for the degreasing of seeds, which significantly increases the percentage of their germination. For this, the seed is soaked for a day in water. Then they are transferred to containers with wet sand. Its humidity must be constantly monitored and prevented from drying out. For convenience, it is better to use glass containers. The containers are put for 2-3 months in a refrigerator or other cool place where the air temperature is in the range from 0 ° C to + 5 ° C. Periodically, the containers are inspected for seed germination. Such seedlings can already be planted.

- Sowing and growing seedlings. At home, seedlings can be grown in glasses or boxes with a volume of 250-300 ml in a substrate based on peat for coniferous crops. A drainage layer is also required. You can prepare the substrate at home yourself. This will require washed sand (3 kg), deoxidized peat (10 kg), dolomite flour or crushed chalk (40-50 g), a handful of ash. The bottom of the tank is covered with a drainage layer, the prepared mixture is placed on it and the box is placed on the pallet. Water well and wait until the substrate absorbs moisture, and excess water is drained. In each box, a recess is made and 2-3 seeds are placed there. A layer of sand (1.5 cm) or a mixture of peat with sawdust is poured on top. To germinate faster, you can create greenhouse conditions at home (cover with film, glass, etc.)

- Sprouted seedlings in the spring are taken out into the street in a warm (non-hot) place, increased watering and left until late autumn. The containers are pre-covered with a film and holes are made in it so that the seedlings breathe. For the winter they are brought into the room. Two-year-old seedlings are planted in a permanent place in late April or early May.

Open soils for planting seedlings are prepared in advance. Humus is added, perlite or sand is added to too dense soils and mixed thoroughly. All compositions of the substrates lime. Between the rows it is necessary to observe a distance of more than 15-18 cm. Sprinkle with a mixture of sand and peat on top (1: 3). After sowing the seeds, the soil is slightly compacted and mulched.
Important! Larch seedlings are especially vulnerable in the first 2-3 months of life and may die. Therefore, they require competent care.
How larch reproduces in nature
In the wild, conifer propagates by layering. The shoots that lay on the ground, and sprinkled on top of them with a substrate or they are surrounded by a moist lichen, take root.
At home, it is best to grow larch seedlings from seeds. To do this, prepare the substrate and a warm room. Provide constant soil moisture and good care. Shoots sprout quickly and are ready for planting in the open ground by the second year of life.