Potatoes are grown in almost every suburban area, and the condition of the tops of this crop can tell a lot about plant health and the volume of the future crop. But sometimes the green leaves of potatoes grow too large or, conversely, can prematurely disappear and fall to the ground, causing a decrease in yield. More details about the important functions of the tops, the reasons for its increased growth and lodging, as well as methods for saving the tuber crop, are further in the article.
The benefits and harms of potato tops
The appearance and size of potato tops signal the gardener about normal growth rates of the bush and the optimal ratio of nutrients in the soil. Leaves play an important role in the life of each plant, but in some cases, intensive growth of green mass can reduce potato yields.
- The main useful properties of the tops are listed below:
- implements the process of photosynthesis, stimulating the growth of tubers;
- saturates root vegetables with nutrients, giving them an excellent taste;
- signals the ripening of the crop, while acquiring a yellow color;
- facilitates pulling the bush from the ground during potato harvesting;
- It is an indicator of plant damage by diseases and pests;
- a change in the appearance of the leaves indicates a lack of fertilizers in the soil, which allows timely feeding and correcting the situation.
- But besides numerous positive qualities, potato tops can be harmful:
- pests and pathogens of various diseases multiply on the leaves, which can cause damage to the crop;
- green tops prevents the appearance of a dense peel on the surface of the potato, providing long-term storage of root crops;
- leaves pull out all the juices from the bush and obscure the soil around the plant, slowing the maturation of potatoes;
- long stems interfere with the digging of potatoes, blocking the row with their large size.
Why the tops of the potatoes die and disappear
At the stage of potato ripening, the tops gradually dry up and bend to the ground. This natural process signals that the root crops are covered with a dense skin and are ready for long-term storage. But sometimes the green mass of the bushes can turn yellow and lie much earlier than the crop ripens, which indicates the presence of a certain problem.
Did you know? In 1995, potatoes were first grown in space aboard the Columbia spacecraft.
The main causes of premature drying of potato tops are presented below:
- late blight - the disease is accompanied by blackening and drying of the leaves, and then the fungus passes to the tubers. Affected stems must be removed and destroyed;
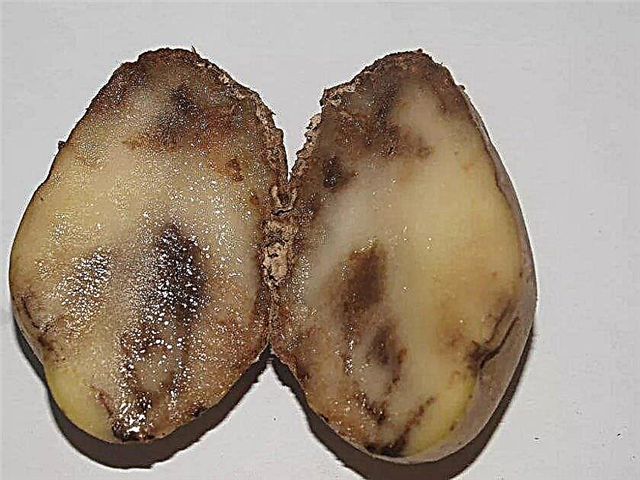
- alternariosis and macrosporiosis - their signs are characteristic spots with a yellow border on the leaves of the bush, and treatment should be carried out using the drug Fitosporin;

- fusarium - manifests itself by the gradual drying of the upper part of the bush, and to eliminate the infection, you need to remove the affected tops and treat the beds with antifungal agents;

- ring rot - the top of the bush turns yellow and twists, and circular stripes of rot appear on the pulp of the tubers. Affected bushes are subject to immediate destruction, and plantings are sprayed with copper-containing preparations to stop the spread of infection;
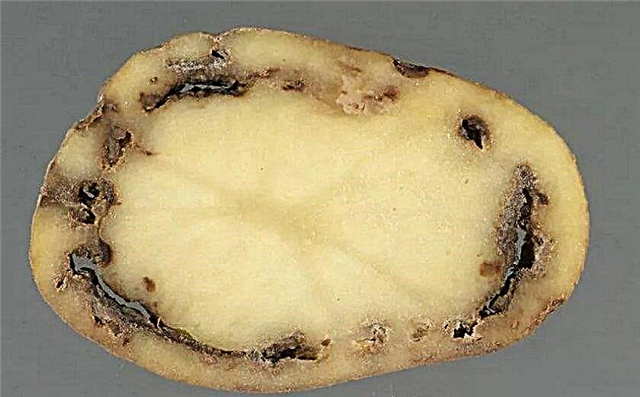
- blackleg - the base of the stem of the bush rots, and its top turns yellow and falls to the ground. To treat the disease, the soil around the plants is sprinkled with a mixture of 1 kg of wood ash and 2 tbsp. l copper sulfate;

- viral diseases (Gothic, leaf curling virus, mottling, etc.) - are accompanied by yellowing of the tops and deformation of tubers, and to fight the infection, you need to destroy the diseased plant and treat the beds with a solution Zircon;

- nematodes - live near the roots of the bush and feed on leaf juices, as a result of which the green mass of the plant is covered with small black dots and lies on the ground. To eliminate the problem, the beds are treated with special chemicals;
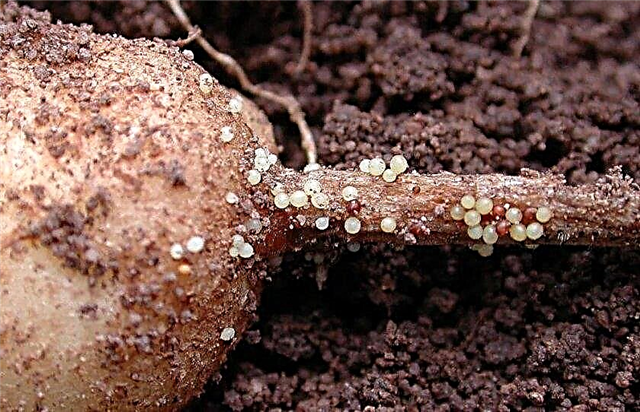

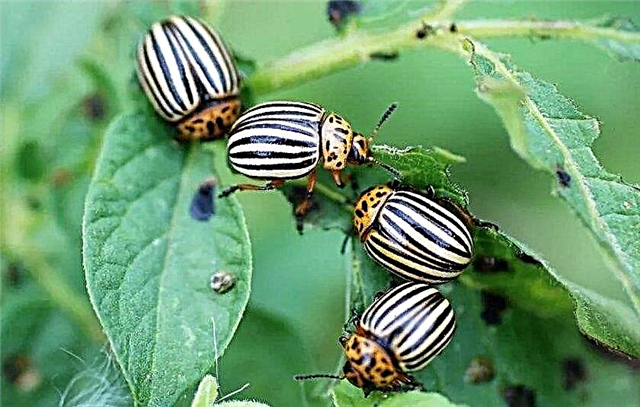
- Colorado potato beetle and other insect pests - feed on leaves and lead to their wilting, causing enormous damage to the crop. To combat them, special chemical insect repellents are used;

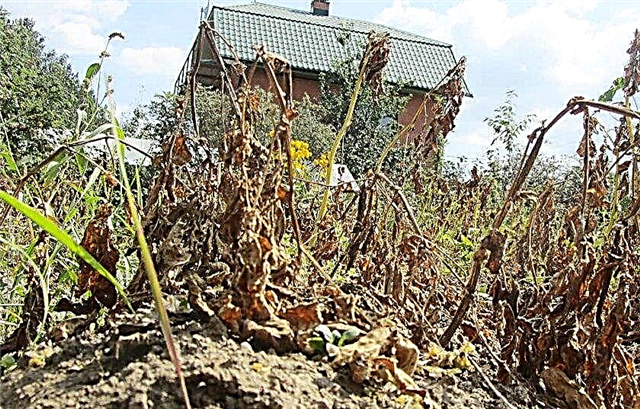
- lack of moisture in the soil - under the bright rays of the sun, the potato wilts during a prolonged drought, so the plants need additional watering;

- soil nutrient deficiency - yellowing, twisting and lodging of tops can indicate a deficiency of magnesium, iron, potassium, phosphorus and nitrogen, so you need to feed plants with fertilizers containing these elements in a timely manner.

The reasons for the appearance of high tops
For some varieties, high tops are quite normal, but with the active growth of powerful green mass in medium-sized varieties of potatoes, the gardener needs to analyze the causes of this phenomenon. The increased growth of tops may indicate a violation of the balance of water and nutrients in the soil, as well as improper conditions for growing crops.
Important! To avoid the appearance of all these problems, you need to adhere to the schedules of watering and fertilizing the crop, observe crop rotation, and also carry out preventive treatment of the site from diseases and pests.
As a result, the plant spends energy on the formation of green mass, and the potato tubers become small, which leads to a decrease in yield. The main reasons for the appearance of high green mass in potatoes are listed below.
Excess moisture, fertilizers
One of the most common causes of the appearance of high tops in potatoes is an excess of nitrogen in the soil. It is formed as a result of improper application of fertilizing containing such substances:
- humus;
- manure;
- bird droppings;
- mullein;
- compost.
When the soil is saturated with nitrogen, the stems grow actively in height, but the formation and maturation of tubers slows down. Therefore, when growing crops, nitrogen-containing fertilizers are recommended to be applied to the plot only in a limited amount.

Sometimes the tops can grow rapidly as a result of abundant watering of beds with potatoes. The soil is oversaturated with moisture, which stimulates the active growth of all green vegetation. At the same time, the plant does not have the strength to form large root crops, and with a strong saturation of the soil with moisture, they can even rot during storage.
Large planting material
For planting potatoes, it is recommended to use medium-sized tubers, but some novice gardeners mistakenly believe that the larger the planting material, the greater the yield.

The main features of the germination of potatoes from large seeds are listed below:
- a green sprout emerging from a tuber needs nutrients, the source of which is seed material;
- a large root crop contains a large supply of the elements necessary for plant growth, so the potato sprouts begin to rapidly reach up;
- potatoes begin to form young root crops only after the supply of nutrients in the seed tuber has run out and the tops have stopped growing;
- as a result of planting large potatoes, the plant spends most of the time growing tops, and new tubers do not have time to form and ripen by the time of harvest.
Important! For planting potatoes, it is recommended to use only intact tubers of the correct shape the size of a chicken egg.
Low light
Potato sprouts need enough light, which the plant needs for normal development. With insufficient illumination of the beds, the leaves of the crop begin to stretch upward in search of sunlight, and there are no resources left for the formation of root crops in the plant. As a result, the tops are high, and the tubers are small.

Insufficient illumination of beds with potatoes can occur in such cases:
- non-compliance with the distance between plants when planting - for each variety there is a recommended arrangement of bushes that allows them to grow normally and not interfere with each other;
- planting crops on a shady area - there is almost no sun in such a place, so potatoes are pulled up;
- a large number of weeds in the beds - they quickly drown out the young sprouts, blocking their access to sunlight.
Climatic conditions
Sometimes potato tops can grow actively under certain weather conditions. For normal development, plants need an air temperature of about +21 ... + 25 ° C and a moderate amount of precipitation. But if the summer often has warm and rainy weather, then all the vegetation, including potatoes, is rapidly extended in height.
Fertilizers to combat tops
Inexperienced gardeners often do not know what to do to combat the active growth of tops. To slow down the growth of the surface of the bush and stimulate the formation of tubers, it is recommended to use various techniques.

With their help, you can restore the normal balance of nutrients in the soil, as well as stop the active growth of green mass and save the crop. The main ways to combat the high green mass of potatoes are listed further in the article.
Superphosphate
It is possible to stop the active growth of the green mass of potatoes and stimulate the formation of young tubers by feeding with superphosphate. Its use is especially effective if the growth of the tops is caused by an excess of nitrogen in the soil. Superphosphate promotes the movement of nutrients from the lush green mass to the roots, and also accelerates the formation and maturation of root crops.
Did you know? The largest potato tuber was grown in 2010 in Nottinghamshire (England) - its weight was 3.8 kg.
Features of the use of this substance are listed below:
- to prepare liquid fertilizer, 100 g of superphosphate and 10 l of hot water are mixed;
- potato bushes are watered with a cooled mixture, spending 1 liter of solution for every 10 m of area;
- for a faster effect, you can spray the green tops of the bushes with a solution of superphosphate.
Limit the amount of nitrogen and mineral fertilizers
To avoid the active growth of tops as a result of an excess of nitrogen in the soil, it is necessary to limit its application, giving preference tofertilizers with potassium and phosphorus, which stimulate the formation and growth of tubers.

The main recommendations for feeding are listed below:
- fertilizers containing nitrogen should be applied only during autumn digging up the soil or spring plowing - 5 buckets of compost or humus per 1 m²;
- if the soil was not fertilized with nitrogen in autumn and early spring, then after the first green shoots appear the plants are fed with a solution of 15 g of urea and 10 l of water - the resulting mixture is enough to process 1 m² of beds;
- after earthing up potatoes per 1 m², 20-30 g of nitrophoska are added, scattering the substance between the rows.
Did you know? On the island of Noirmoutier (France) they cultivate a variety of potatoes La Bonnotte, which is recognized as the most expensive in the world due to its excellent taste and especially delicate pulp.
To avoid saturation of the soil with fertilizers, it is not recommended to introduce other root top dressings. In the presence of high tops and with a large number of mineral fertilizers, even large tubers will be poorly stored.
Tops removal
To slow the rapid growth of tops and stimulate the formation of root crops, the green mass can be gently bent to the ground without breaking the stems of the bush. This method allows you to save the crop in cases where the reasons for the increased growth of the ground part of the bush cannot be precisely determined.

Features of the removal of the surface of the potato are listed below:
- first cut off the upper part of plants at a height of 25 cm above the surface of the earth - this stops the growth of the bush and contributes to better absorption of chemicals by it;
- a day after pruning, the tops of the beds are treated with special chemicals - they affect the remaining part of the green stem of the bush, causing it to dry out, as a result of which the plant spends energy only on the formation of tubers;
- It is recommended to remove the tops about a week before the green mass is completely mowed.
Mowing
Some gardeners recommend mowing the tops immediately after the plant fades. The process of tuber formation begins at the stage of the appearance of buds on the bush and continues until flowering is completed. After this, the formed root crops begin to increase in size, ripening at the time of harvest.

Mowing is carried out 3-4 weeks after the completion of flowering crops and 2-3 weeks before harvesting. This procedure not only stops the growth of green mass, but also has a beneficial effect on the volume and quality of the crop:
- stimulates the growth of root crops;
- potatoes faster covered with a dense peel, necessary for long-term storage;
- tubers are actively saturated with nutrients, becoming more delicious;
- the soil on the beds is better warmed up by the rays of the sun, which has a beneficial effect on the timing of the ripening of the crop;
- the likelihood of diseases and pests affecting the tops of the plant is reduced.
Important! To prevent the multiplication of pathogens and pests in the soil, after mowing the tops, you need to take it out of the site, and treat the soil with fungicides.
To get a generous potato crop, you need to monitor the condition of the tops of the bushes in order to notice the signs of its active growth or drying in time. Using the recommendations listed in this article, you can accurately determine the cause of the problem and eliminate it at an early stage, preventing significant crop losses.






















